 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
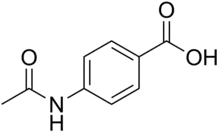
4-Acetamidobenzoic acid | |
| Other names
N-Acetyl-PABA; 4-Carboxyacetanilide; p-Acetamidobenzoic acid
p-Acetaminobenzoic acid; PAAB; p-Acetoaminobenzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.287 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H9NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 179.175 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 259 to 262 °C (498 to 504 °F; 532 to 535 K) (dec.) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Acedoben (4-acetamidobenzoic acid or N-acetyl-PABA) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula of C9H9NO3. It is the acetyl derivative of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA).
Acedoben, as a salt with dimepranol, is a component of some pharmaceutical preparations such as inosine pranobex.
See also
- N-Acetylanthranilic acid is an positional isomer of this compound
References
- ↑ "4-Acetamidobenzoic acid". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ Acedoben, ChemIndustry.com
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.