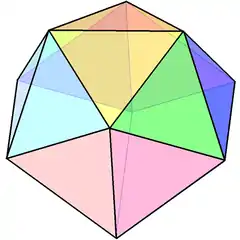
| Edge-contracted icosahedron | |
|---|---|
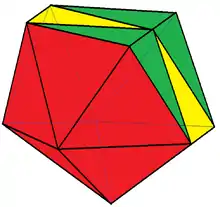 | |
| Type | Octadecahedron |
| Faces | 18 triangles |
| Edges | 27 |
| Vertices | 11 |
| Vertex configuration | 2 (34) 8 (35) 1 (36) |
| Symmetry group | C2v, [2], (*22), order 4 |
| Properties | Convex, deltahedron |
| Net | |
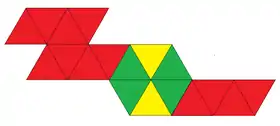 | |
In geometry, an edge-contracted icosahedron is a polyhedron with 18 triangular faces, 27 edges, and 11 vertices.
Construction
It can be constructed from the regular icosahedron, with one edge contraction, removing one vertex, 3 edges, and 2 faces. This contraction distorts the circumscribed sphere original vertices. With all equilateral triangle faces, it has 2 sets of 3 coplanar equilateral triangles (each forming a half-hexagon), and thus is not a Johnson solid.
If the sets of three coplanar triangles are considered a single face (called a triamond[1]), it has 10 vertices, 22 edges, and 14 faces, 12 triangles ![]() and 2 triamonds
and 2 triamonds ![]() .
.
It may also be described as having a hybrid square-pentagonal antiprismatic core (an antiprismatic core with one square base and one pentagonal base); each base is then augmented with a pyramid.
Related polytopes
The dissected regular icosahedron is a variant topologically equivalent to the sphenocorona with the two sets of 3 coplanar faces as trapezoids. This is the vertex figure of a 4D polytope, grand antiprism. It has 10 vertices, 22 edges, and 12 equilateral triangular faces and 2 trapezoid faces.[2]
In chemistry
In chemistry, this polyhedron is most commonly called the octadecahedron, for 18 triangular faces, and represents the closo-boranate [B11H11]2−. [3]
-dianion-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png.webp) Ball-and-stick model of the closo-undecaborate ion, [B11H11]2− |
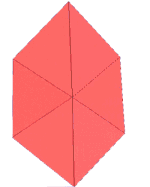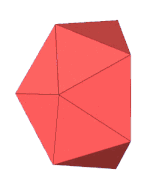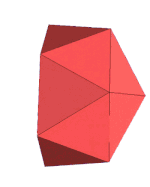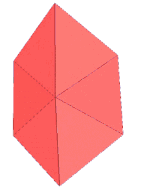 closo-boranate [B11H11]2− |
 Net |
Related polyhedra
The elongated octahedron is similar to the edge-contracted icosahedron, but instead of only one edge contracted, two opposite edges are contracted.
References
- ↑ "Convex Triamond Regular Polyhedra".
- ↑ John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 26) The Grand Antiprism
- ↑ Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, p. 1165, ISBN 0-12-352651-5