 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-2-oxopropanoic acid | |
| Other names
Hydroxypyruvate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1721079 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.124.121 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 104.06 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 202 °C (396 °F; 475 K) |
| Hazards[1] | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H302, H314 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P330, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
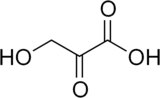
Hydroxypyruvic acid is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2C(O)CO2H. It is a white solid. It is encountered in many biochemical contexts, being the oxidized derivative of lactic acid, a degradation product of RuBisCO, and the result of oxidative deamination of serine.[2]
See also
Notes
- ↑ "3-Hydroxypyruvic acid". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ Timm, Stefan; Florian, Alexandra; Jahnke, Kathrin; Nunes-Nesi, Adriano; Fernie, Alisdair R.; Bauwe, Hermann (2011). "The Hydroxypyruvate-Reducing System in Arabidopsis: Multiple Enzymes for the Same End". Plant Physiology. 155 (2): 694–705. doi:10.1104/pp.110.166538. PMC 3032460. PMID 21205613.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.