| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Libra |
| Right ascension | 14h 34m 16.81166s[2] |
| Declination | −12° 31′ 10.4145″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.32[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M4.0V[4] |
| B−V color index | 1.633±0.052[3] |
| Variable type | BY Dra |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −1.36±0.20[2] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −355.138 mas/yr[2] Dec.: 593.040 mas/yr[2] |
| Parallax (π) | 159.9225 ± 0.0546 mas[2] |
| Distance | 20.395 ± 0.007 ly (6.253 ± 0.002 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 12.41[3] |
| Details[4] | |
| Mass | 0.291±0.013 M☉ |
| Radius | 0.299±0.009 R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 0.010106±0.000069 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.76±0.13 cgs |
| Temperature | 3347±50 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.18±0.15 dex |
| Rotation | 96±2 d |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | <2.0 km/s |
| Age | 0.8–8.0 Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
 Gliese 555 Location of Gliese 555 in the constellation Libra | |
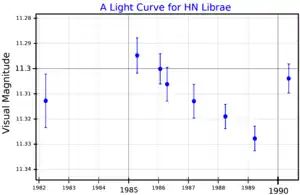
Gliese 555 is a small star with one or more orbiting exoplanets in the constellation Libra. It has the variable star designation HN Librae, abbreviated HM Lib. With an apparent visual magnitude of 11.32,[3] it can only be viewed through a telescope. The system is located at a distance of 20.4 light years based on parallax measurements, but is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −1.4 km/s.[2] It does not appear to belong to any known stellar moving group or association.[4]
This is an M-type main-sequence star, a red dwarf, with a stellar classification of M4.0V. The chromosphere of this star is weakly active, causing starspots that vary the stellar luminosity as it rotates.[4] It has 29% of the mass of the Sun and 30% of the Sun's girth. On average, the star is radiating just 1% of the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,347 K. The star is spinning slowly with a rotation period of around 96 days.[4]
Planetary system
In 2019, one planet candidate detected by radial velocity was reported in a preprint, among 118 planets around M dwarf stars. This would have a minimum mass about 30 times that of Earth and orbit with a period of about 450 days.[6]
However, later radial velocity observations by the CARMENES survey published in 2023 did not confirm a planet at this period, but instead found a different planet.[7] This is a super-Earth or mini-Neptune (the discovery paper uses the term "sub-Neptune") with a minimum mass of 5.5 Earths and a period of 36 days, placing it within the habitable zone. A second planet candidate was also found, with a minimum mass of 9.7 Earths and a period of 113 days, but this signal could not be confirmed as having a planetary origin due to its similarity to the rotation period of the star.[4]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | ≥5.46±0.75 M🜨 | 0.1417±0.0023 | 36.116+0.027 −0.029 |
0.079+0.090 −0.055 |
— | — |
| c (unconfirmed) | ≥9.7±1.9 M⊕ | 0.3040+0.0048 −0.0051 |
113.46+0.19 −0.20 |
— | — | — |
References
- ↑ Weis, Edward W. (March 1994). "Long Term Variability in Dwarf M Stars". The Astronomical Journal. 107: 1135–1140. Bibcode:1994AJ....107.1135W. doi:10.1086/116925. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 4 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 González-Álvarez, E.; Kemmer, J.; et al. (July 2023). "The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs. A sub-Neptunian mass planet in the habitable zone of HN Lib". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 675: A141. arXiv:2305.19677. Bibcode:2023A&A...675A.141G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202346276.
- ↑ "BD-11 3759". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2023-12-09.
- ↑ Barnes, J. R.; et al. (2019-06-11). "Frequency of planets orbiting M dwarfs in the Solar neighbourhood". arXiv:1906.04644 [astro-ph.EP].
- ↑ Ribas, I.; Reiners, A.; et al. (February 2023). "The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs. Guaranteed time observations Data Release 1 (2016-2020)". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 670: A139. arXiv:2302.10528. Bibcode:2023A&A...670A.139R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202244879.