



In Japan, road signs (道路標識, dōro-hyōshiki) are standardized by the "Order on Road Sign, Road Line, and Road Surface Marking (道路標識、区画線及び道路標示に関する命令)" established in 1968 with origins from the Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department's "Order on Standardization of Road Sign" of 1934 and the Home Ministry of Japan's "Order on Road Signs" of 1942.[1] The previous designs have been used since 1986 after several amendments of order.[2]
They are divided into "Principal Sign" (本標識, hon-hyōshiki) and "Supplemental Sign" (補助標識, hojo-hyōshiki).
Principal signs
Principal signs (本標識, hon-hyōshiki) are categorized into 4 types; guide, warning, regulatory and instruction signs.
Guide signs
Guide signs (案内標識, an'nai-hyōshiki) indicates directions or distances of the road. Guide signs have dark green backgrounds and white text for expressways. In urban areas and on national highways, direction signs have dark blue backgrounds. The signs are normally written in Japanese and English. Since 2014, Vialog is used as the typeface for English words and Place name Transcriptions.
 Expressway ramp ahead
Expressway ramp ahead.svg.png.webp) Expressway exit ahead
Expressway exit ahead.svg.png.webp) Exits and distance (expressway)
Exits and distance (expressway) Junction (expressway)
Junction (expressway) Expressway number (E1; Tomei)
Expressway number (E1; Tomei).svg.png.webp) Expressway shield (E4; Tōhoku)
Expressway shield (E4; Tōhoku)
 Intersection
Intersection Intersection
Intersection Distance of cities and areas
Distance of cities and areas National highway shield (Route 20)
National highway shield (Route 20) National highway shield
National highway shield National highway shield
National highway shield Prefectural highway shield (Fukuoka Route 758)
Prefectural highway shield (Fukuoka Route 758) Prefectural highway shield
Prefectural highway shield Prefectural highway shield (inter-city route)
Prefectural highway shield (inter-city route) Prefectural highway shield
Prefectural highway shield Prefectural highway shield (inter-city route)
Prefectural highway shield (inter-city route) Street name
Street name Detour
Detour Detour
Detour Mitigated limitation of height (expressway)
Mitigated limitation of height (expressway) Mitigated limitation of weight
Mitigated limitation of weight
Warning signs
Warning signs (警戒標識, keikai-hyōshiki) warn drivers of dangers or situations that they must pay attention to. Their design, black pattern and border on yellow diamond (usually with 45 cm per a side), is based on the U.S. MUTCD (due to this nation being part of Major non-NATO ally).[4]
 Crossroads
Crossroads T-intersection with road on the right
T-intersection with road on the right T-junction
T-junction T-intersection with road on the left
T-intersection with road on the left Y-junction
Y-junction Traffic circle
Traffic circle Curve to the right
Curve to the right Curve to the left
Curve to the left Sharp curve to the right
Sharp curve to the right Sharp curve to the left
Sharp curve to the left Double curve, first to the right
Double curve, first to the right Double curve, first to the left
Double curve, first to the left Double sharp, first to the right
Double sharp, first to the right Double sharp, first to the left
Double sharp, first to the left Winding road first curve to the right
Winding road first curve to the right Winding road first curve to the left
Winding road first curve to the left Railroad crossing ahead
Railroad crossing ahead
Option 1: steam locomotive Railroad crossing ahead
Railroad crossing ahead
Option 2: electric train School ahead
School ahead Traffic light ahead
Traffic light ahead Slippery road
Slippery road Fallen rocks
Fallen rocks Bumpy road
Bumpy road Traffic merges from the left
Traffic merges from the left Left lane ends
Left lane ends Road narrows on both sides
Road narrows on both sides Two-way traffic ahead
Two-way traffic ahead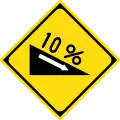 Steep descent (10%, 1:10)
Steep descent (10%, 1:10) Steep ascent (10%, 1:10)
Steep ascent (10%, 1:10) Men at work
Men at work Crosswind
Crosswind Watch for large animals (deer)
Watch for large animals (deer) Watch for large animals (rabbit)
Watch for large animals (rabbit) Watch for large animals (monkey)
Watch for large animals (monkey) Watch for large animals (raccoon dogs)
Watch for large animals (raccoon dogs) Be careful
Be careful
Regulatory signs
Regulatory signs (規制標識, kisei-hyōshiki) show the regulations of each roads in order to keep road condition and prevent dangers of traffic.
The stop sign is a red, downward-pointing triangle, with the text 止まれ (tomare) & "stop" (in English, for the pre-1963 and current designs only) in white. Prohibition signs are round with white backgrounds, red borders, and blue pictograms. Mandatory instruction signs are round with blue backgrounds and white pictograms.
- Stop and slow down
 Slow down (In Japanese and English, current design from 2017)
Slow down (In Japanese and English, current design from 2017) Slow down (In Japanese Only, phased out in 2017)
Slow down (In Japanese Only, phased out in 2017) Yield (In Japanese Only, phased out in 2017)
Yield (In Japanese Only, phased out in 2017) Stop (In Japanese and English, current design from 2017)
Stop (In Japanese and English, current design from 2017) Stop (In Japanese Only, used from 1963 to 2017)
Stop (In Japanese Only, used from 1963 to 2017).svg.png.webp) Stop (In English Only, used in United States Armed Forces Bases in Japan.)
Stop (In English Only, used in United States Armed Forces Bases in Japan.).svg.png.webp) Stop sign, used from 1950 to 1960
Stop sign, used from 1950 to 1960.svg.png.webp) Stop sign, used from 1960 to 1963
Stop sign, used from 1960 to 1963
- Exclusions
 Road closed to all
Road closed to all Road closed to vehicles
Road closed to vehicles No entry
No entry No motor vehicles except motorcycles and mopeds
No motor vehicles except motorcycles and mopeds No trucks
No trucks No buses
No buses No motorbikes or mopeds
No motorbikes or mopeds No non-motorized vehicles except bicycles
No non-motorized vehicles except bicycles No bicycles
No bicycles No motor vehicles
No motor vehicles No two-person motorbikes or mopeds
No two-person motorbikes or mopeds No vehicles carrying dangerous goods
No vehicles carrying dangerous goods Weight limit
Weight limit Height limit
Height limit Width limit
Width limit Motor vehicles only(Except mopeds)
Motor vehicles only(Except mopeds) Bicycles only
Bicycles only Bicycles and pedestrians only
Bicycles and pedestrians only Pedestrians only
Pedestrians only Road closed to pedestrians
Road closed to pedestrians
- Turns
 Only straight ahead or left turn permitted
Only straight ahead or left turn permitted Only straight ahead or right turn permitted
Only straight ahead or right turn permitted Turn left
Turn left Turn right
Turn right No turns
No turns Turn left or right
Turn left or right Directions permitted
Directions permitted Roundabout
Roundabout Keep left
Keep left Keep right
Keep right No crossing center line to enter e.g. a car park
No crossing center line to enter e.g. a car park No U-turn
No U-turn Two-stage right turn for mopeds & bicycles required.
Two-stage right turn for mopeds & bicycles required. Two-stage right turn for mopeds & bicycles NOT required.
Two-stage right turn for mopeds & bicycles NOT required.
- Restrictions
 No crossing center line to overtake. 追越し禁止 sign below = NO passing at all
No crossing center line to overtake. 追越し禁止 sign below = NO passing at all.svg.png.webp) Speed limit
Speed limit_and_507-C.svg.png.webp) End of special speed limit
End of special speed limit
The statutory speed limit applies_and_507-A.svg.png.webp) End of speed restriction limit[5]
End of speed restriction limit[5].svg.png.webp) Minimum speed limit
Minimum speed limit One-way street to the left
One-way street to the left One way street to the right
One way street to the right One-way street ahead
One-way street ahead One way (bikes)
One way (bikes) Trucks use left lane[6]
Trucks use left lane[6] Buses-only lane
Buses-only lane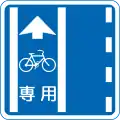 Bike lane
Bike lane Buses-priority lane
Buses-priority lane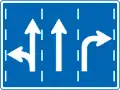 Lane usage
Lane usage Lane usage
Lane usage Lane usage
Lane usage Lane usage
Lane usage Use car horns
Use car horns No jaywalking
No jaywalking
- Parking and stopping
 No stopping
No stopping No parking
No parking Restricted parking
Restricted parking Parallel parking
Parallel parking Perpendicular parking
Perpendicular parking Angle parking
Angle parking
Instruction signs
Instruction signs (指示標識, shiji-hyōshiki) show points and devices on the road that drivers should pay attention.
 Cyclists are permitted to ride side-by-side.
Cyclists are permitted to ride side-by-side. Driving on tram line permitted (Except two-wheelers)
Driving on tram line permitted (Except two-wheelers) Priority road
Priority road Center line
Center line Stop line
Stop line.svg.png.webp) Parking zone
Parking zone Stopping permitted
Stopping permitted Crosswalk
Crosswalk
Alt. A Crosswalk
Crosswalk
Alt. B: school zone Bike crossing
Bike crossing Bike and crosswalk
Bike and crosswalk
 Controls ahead
Controls ahead
Supplemental signs
Supplemental signs (補助標識, hojo-hyōshiki) are usually put just below the principal signs, and shows their valid range like time, day and category of vehicle.[7] They are equivalent to the "plaque" of the American MUTCD. The width of the plates is usually 60 cm, and the sentences should be less than 7 characters per a line or 3 lines.[8] When the sentences can not be shortened less than the limitation, they should apply changeable signs.[8]
 100 meters ahead
100 meters ahead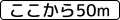 Next 50 meters
Next 50 meters Except Sundays and Holidays
Except Sundays and Holidays 8 a.m. to 8 p.m.
8 a.m. to 8 p.m. Except mopeds
Except mopeds Large trucks
Large trucks Bicycles (symbol)
Bicycles (symbol) Trucks (symbol)
Trucks (symbol)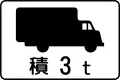 Trucks carrying over 3 tonnes (symbol)
Trucks carrying over 3 tonnes (symbol) Only for permitted vehicles
Only for permitted vehicles Leave at least 6 meters road width clear when you park
Leave at least 6 meters road width clear when you park Permitted until the time the parking meter shows
Permitted until the time the parking meter shows Restriction begins (symbol)
Restriction begins (symbol)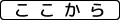 Restriction begins
Restriction begins Restriction begins
Restriction begins Restricted zone (symbol)
Restricted zone (symbol) Restricted zone
Restricted zone End of restriction (symbol)
End of restriction (symbol) End of restriction
End of restriction End of restriction
End of restriction End of restriction
End of restriction School zone
School zone No passing or overtaking
No passing or overtaking Yield
Yield Train crossing caution
Train crossing caution Caution crosswind
Caution crosswind Caution wild animals
Caution wild animals Caution
Caution Safety speed: 30 km/h
Safety speed: 30 km/h Caution soft shoulder
Caution soft shoulder Be quiet
Be quiet direction
direction Control zone: Honmachi, Komoro
Control zone: Honmachi, Komoro Starts
Starts Ends
Ends
Other signs
 Expressway name (Tomei)
Expressway name (Tomei) Asian Highway route shield (AH1)
Asian Highway route shield (AH1).svg.png.webp) Ferry (pictogram established in Japanese Industrial Standards)
Ferry (pictogram established in Japanese Industrial Standards)
History

The first standardised road signage schemes appeared in 1922. At first, two types of signs were established: "road warning signs" equivalent to warning signs and "road guide signs" as information signs.[9] Warning signs at that time closely resembled the British design as used in Hong Kong, the only difference was the white-on-black lettering.
Japanese road signs in the early 1940s closely followed European road signage practices at that time based on the 1931 Geneva Convention, except that most road signages contained text. A variation of the early 1940s Japanese road signage system is still in use today in Taiwan.[9][10]
In 1950, a complete revision of the "Road Signs Ordinance" was promulgated and enforced as an Ordinance of the Prime Minister's Office and the Ministry of Construction. Unlike the 1922 and the 1940s devised road signs, it included both bilingual Japanese and English text and symbols. Warning signs were changed from a European red-bordered triangular design to an American MUTCD yellow diamond design.[9] This road signage system was used until 1963, when it was replaced with a new road signage system that is based on the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. The present-day Japanese road signage system also replaced the stop sign's shape with an inverted equilateral triangle like the stop sign used in West Germany from the 1945 to 1971.[9]

In 2016, it was announced that the Japanese National Police Agency was considering changing the design of the "Stop" sign used on Japanese roads since 1963 from the inverted red triangle sign to an octagonal design more closely conforming to the recommendations of the 1968 Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals.[11] The inverted red triangle sign was introduced in 1963 ahead of the 1964 Summer Olympic Games in Tokyo, and replaced the earlier red octagonal sign used from 1960, which in turn had replaced the yellow octagonal sign used from 1950.[11] It was later decided to make the stop sign bilingual in both Japanese and English, but to maintain the inverted triangular shape.[12]
Photographs
 Street name and highway shields (Chiba Prefecture)
Street name and highway shields (Chiba Prefecture) Expressway exit sign
Expressway exit sign Intersection guide sign
Intersection guide sign.jpg.webp) Height and weight restrictions apply (to streets pointed to by arrows)
Height and weight restrictions apply (to streets pointed to by arrows) Lane usage signs
Lane usage signs Changeable lane usage signs
Changeable lane usage signs Directions permitted
Directions permitted Tram stop
Tram stop Right turn prohibition (7-9 a.m.) ends
Right turn prohibition (7-9 a.m.) ends Taxis without any passengers can not enter from 9 p.m. unit 2 a.m.
Taxis without any passengers can not enter from 9 p.m. unit 2 a.m. Restrictions 200 m ahead
Restrictions 200 m ahead Asian highway sign and symbol of Nihonbashi (Shuto Expressway)
Asian highway sign and symbol of Nihonbashi (Shuto Expressway)
References
- ↑ 時崎賢二 1990, p. 22.
- ↑ dark-RX 2008, p. 105.
- ↑ "Fuenfwerken-Schrift in Japan | Fuenfwerken". www.fuenfwerken.com (in German). Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ↑ 時崎賢二 1979, p. 24.
- ↑ A left arrow or ここまで in the supplemental sign (plaque) means "END". A right arrow or ここから in the plaque means "BEGIN".
- ↑ The symbol can be changed to other vehicles.
- ↑ 全標協 2013, p. 3(設置)
- 1 2 警察庁 2017, p. 32.
- 1 2 3 4 "道路標識の歴史(変遷) | KICTEC". KICTEC | 交通インフラから公共空間まで多彩な快適環境保全創りに挑みます (in Japanese). 2012-06-18. Retrieved 2023-01-24.
- ↑ "旧型道路標識一覧(禁止・指導・規制・警戒標識)". trafficsignal.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2022-09-09.
- 1 2 "Design of Japanese stop signs might change ahead of Olympic tourism surge". The Japan Times. Japan: The Japan Times Ltd. 21 January 2016. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- ↑ "英語併記の新標識お目見え 一時停止に「STOP」". 日本経済新聞 電子版 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2018-01-24.
Bibliography
- 時崎賢二 (1979). "道路標識等の基礎知識". 月刊交通. 東京法令出版. 10 (5): 18–29.
- 時崎賢二 (1990). "道路標識の国際化". 月刊交通. 東京法令出版. 21 (4): 19–39.
- dark-RX (2008-03-20). "見つけよう! 旧標識". 酷道をゆく. イカロス出版: 104–107. ISBN 978-4-86320-025-8.
- 全国道路標識標示業協会(編) (2013). 道路標識ハンドブック (2012年度版 ed.). 全国道路標識・標示業協会.
- 警察庁交通局 (2017-04-24). "交通規制基準" (PDF). 警察庁. Retrieved 2017-11-08.
- "道路標識、区画線及び道路標示に関する命令 別表第2". www.mlit.go.jp. Retrieved 2018-01-24.
- "17062814_ichiran(止まれ、徐行正式版追加)" (PDF). www.mlit.go.jp (PDF). 2017-06-28. Retrieved 2018-01-25.