 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Disodium hydroxybutanedioate | |
| Other names
Disodium malate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.571 |
| E number | E350i (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
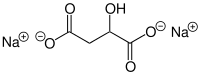
| C4H4Na2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 178.051 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Sodium malate is a compound with formula Na2(C2H4O(COO)2). It is the sodium salt of malic acid. As a food additive, it has the E number E350.[1]
Properties
Sodium malate is an odorless white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water.[2]
Use
It is used as an acidity regulator and flavoring agent.[2] It tastes similar to sodium chloride (table salt).[3]
References
- ↑ Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers, Food Standards Agency, 11 January 2017
- 1 2 Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Meeting, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation. (2006). Compendium of Food Additive Specifications. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. pp. 49–50. ISBN 92-5-105559-9.
- ↑ Whitmore, Frank C. (2012). Organic Chemistry, Volume One : Part I: Aliphatic Compounds (2nd ed.). Mineola, New York: Dover Publications. p. 397. ISBN 9780486311159.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.