| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquila |
| Right ascension | 19h 33m 46.031s[2] |
| Declination | +05° 27′ 56.54″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.48 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M5-5.5III |
| B−V color index | 1.471 |
| Variable type | Semiregular |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 3 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −5.26 ± 0.53[2] mas/yr Dec.: −24.24 ± 0.32[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 4.94 ± 0.47 mas[2] |
| Distance | 660 ± 60 ly (200 ± 20 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.87 |
| Details | |
| Luminosity | 2172[3] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3326[3] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
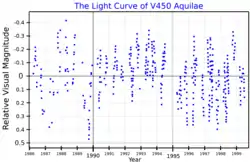
V450 Aquilae is semi-regular pulsating star in the constellation Aquila. Located around 660 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity approximately 2172 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 3326 K.[3]
References
- ↑ Percy, John R.; Wilson, Joseph B.; Henry, Gregory W. (August 2001). "Long-Term VRI Photometry of Small-Amplitude Red Variables. I. Light Curves and Periods". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 113 (786): 983–996. Bibcode:2001PASP..113..983P. doi:10.1086/322153. S2CID 14609175.
- 1 2 3 4 5 van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600.Vizier catalog entry
- 1 2 3 McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (2012). "Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 427 (1): 343–57. arXiv:1208.2037. Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x. S2CID 118665352.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.